Arthritis of the Shoulder
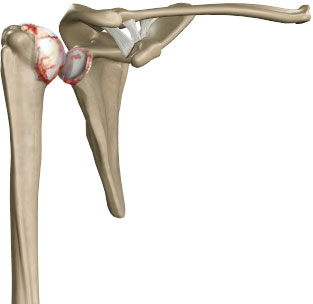
The term arthritis literally means inflammation of a joint, but is generally used to describe any condition in which there is damage to the cartilage. Damage of the cartilage in the shoulder joint causes shoulder arthritis. Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury. The warning signs that inflammation presents are redness, swelling, heat and pain.
The cartilage is a padding that absorbs stress. The proportion of cartilage damage and synovial inflammation varies with the type and stage of arthritis. Usually the pain early on is due to inflammation. In the later stages, when the cartilage is worn away, most of the pain comes from the mechanical friction of raw bones rubbing on each other.
Types of Arthritis
There are over 100 different types of rheumatic diseases. The most common are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is also called as degenerative joint disease; this is the most common type of arthritis, which occurs often in older people. This disease affects cartilage, the tissue that cushions and protects the ends of bones in a joint. With osteoarthritis, the cartilage starts to wear away over time. In extreme cases, the cartilage can completely wear away, leaving nothing to protect the bones in a joint, causing bone-on-bone contact. Bones may also bulge, or stick out at the end of a joint, called a bone spur.
Osteoarthritis causes joint pain and can limit a person's normal range of motion (the ability to freely move and bend a joint). When severe, the shoulder joint may lose all movement, making a person disabled.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: This is an auto-immune disease in which the body's immune system (the body's way of fighting infection) attacks healthy joints, tissues, and organs. Occurring most often in women of childbearing age (15-44), this disease inflames the lining (or synovium) of joints. It can cause pain, stiffness, swelling, and loss of function in joints. When severe, rheumatoid arthritis can deform, or change, a joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects mostly joints of the hands and feet and tends to be symmetrical. This means the disease affects the same joints on both sides of the body (both the hands or both feet) at the same time and with the same symptoms. No other form of arthritis is symmetrical. About two to three times as many women as men have this disease.
Causes
Osteoarthritis is caused by the wearing out of the cartilage covering the bone ends in a joint. This may be due to excessive strain over prolonged periods of time, or due to other joint diseases, injury or deformity. Primary osteoarthritis is commonly associated with ageing and general degeneration of joints.
Secondary osteoarthritis is generally the consequence of another disease or condition, such as repeated trauma or surgery to the affected joint, or abnormal joint structures from birth.
Rheumatoid arthritis is often caused when the genes responsible for the disease is triggered by infection or any environmental factors. With this trigger body produce antibodies, the defense mechanism of body, against the joint and may cause rheumatoid arthritis.
Symptoms
There are several forms of arthritis and the symptoms vary according to the form of arthritis. Each form affects the body differently. Arthritic symptoms generally include swelling and pain or tenderness in joints for more than two weeks, redness or heat in a joint, limitation of motion of a joint, and early morning stiffness.
In an arthritic shoulder
- The cartilage lining is thinner than normal or completely absent. The degree of cartilage damage and inflammation varies with the type and stage of arthritis
- The capsule of the arthritic shoulder is swollen
- The joint space is narrowed and irregular in outline; this can be seen in an X-ray image.
- Bone spurs or excessive bone can also build up around the edges of the joint
Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose arthritis with a medical history, physical exam and X-rays of the affected part. Computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are also performed to diagnose arthritis.
Treatment Options
There is no cure for arthritis, so beware of 'miracle cures'. Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medicine. They may recommend occupational therapy or physiotherapy, which includes exercises and heat treatment. In severe cases, surgery may be suggested. The type of surgery will depend on your age and severity of the disease. In the elderly with severe arthritis, joint replacement can give good results. Common surgery for treatment of shoulder arthritis arthroplasty (replacement of the damaged joint) may be total shoulder arthroplasty or hemiarthroplasty.









